

I heard that Bitcoin uses a mechanism that has never been used before, what does that mean?
Bitcoin is a new form of money that is not controlled by any particular country or bank.
It has completely different properties from conventional currencies, and is being developed in many countries around the world.
In this article, I'll introduce how bitcoin works in an easy-to-understand way for beginners.


Supervisor: Koji Higashi
A pioneering figure in the domestic industry, engaged in Bitcoin-related businesses since the early days in 2014.
Co-founder of Diamond Hands/Operator of the YouTube channel "Bitcoiner's Hanseikai".
This article was written in Japanese and converted to English using a translation tool.
Date of writing (Japanese version): January 2024
An easy-to-understand explanation of how bitcoin works [for beginners]


Bitcoin isn't run by one company, like "Bitcoin Inc!
ここからはビットコインの仕組みについて、1つずつ分かりやすく解説するよ。

- Decentralized network with no central manager
- Blockchain technology is difficult to tamper with
- Transactions are open to the public
Decentralized network with no central controller
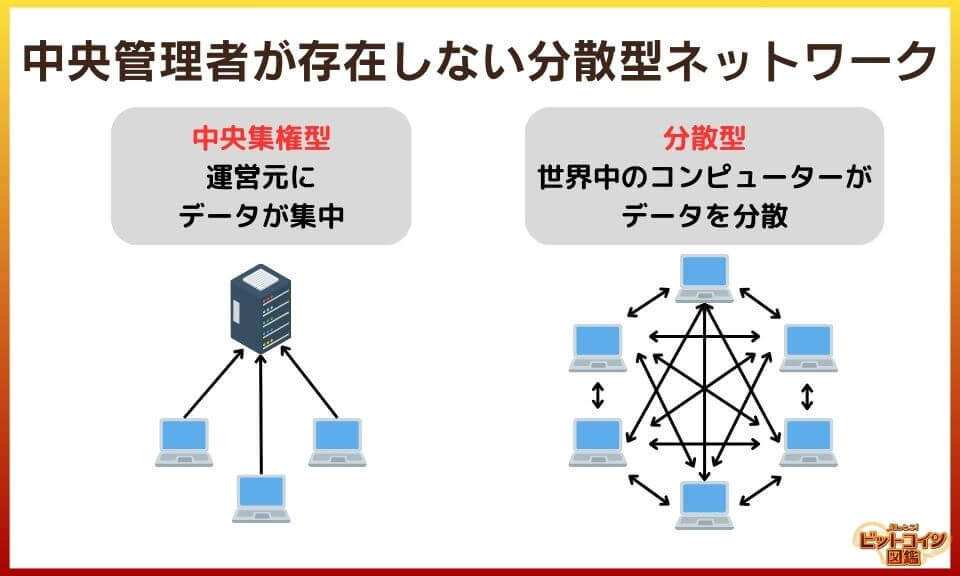
Bitcoin uses a decentralized network in which there is no central administrator such as a central bank or company.
Decentralized…used to mean the opposite of centralized (power concentrated in one place).
In the decentralized network of Bitcoin, many computers are connected via the Internet.
More than 10,000 nodes (computers) scattered around the world verify bitcoin transactions.
Bitcoin's decentralized network
- A network that belongs to no one
→All participants operate jointly, and no one person or organization can control everything - Anyone can participate
→ Anyone can join or leave the bitcoin network at will - Decisions are made jointly
→Consensus of many nodes is required to change the rules of the network. Also, if one node fails, the entire network continues to operate correctly

No administrator means that one big company isn't going to put it all together, right?
Some people might not follow the rules, and I wonder if it would really work.
In the bitcoin network, if you violate the rules, you don't get paid, and if you follow the rules and contribute to the network, you get paid.
The incentive to follow the rules is one of the reasons why Bitcoin works so well.

Blockchain technology difficult to tamper with
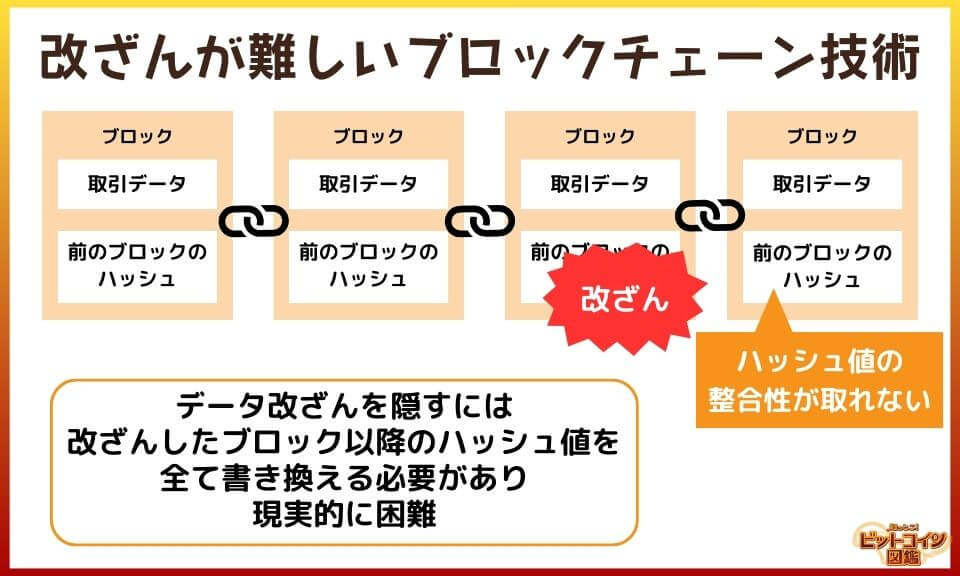
Blockchain is a technology for recording digital data, consisting of collections of data called "blocks" that are connected like a "chain.
Multiple transaction records are contained in each block, and each is linked in time order.
Once data is recorded in a block, it is extremely difficult to tamper with.
Reasons why data tampering is difficult (example)
- Distributed network
→Operated by computers (nodes) around the world, each node has a copy of the blockchain, so if one node is tampered with, other nodes are not affected. - Use of hash values
→ An irregular string of converted data. If the data changes even slightly, the hash value also changes significantly, allowing tampering to be detected. - Consensus mechanism (Proof of Work/PoW)
→Generating a new block is computationally very difficult, and adding a block requires the agreement of a large portion of the network
To tamper with one piece of data, you have to tamper with all the blocks in a row.
Bitcoin is a combination of several other technologies that make tampering infinitely more difficult.


So the system doesn't allow someone to rewrite transaction records without permission!
Transactions are public.
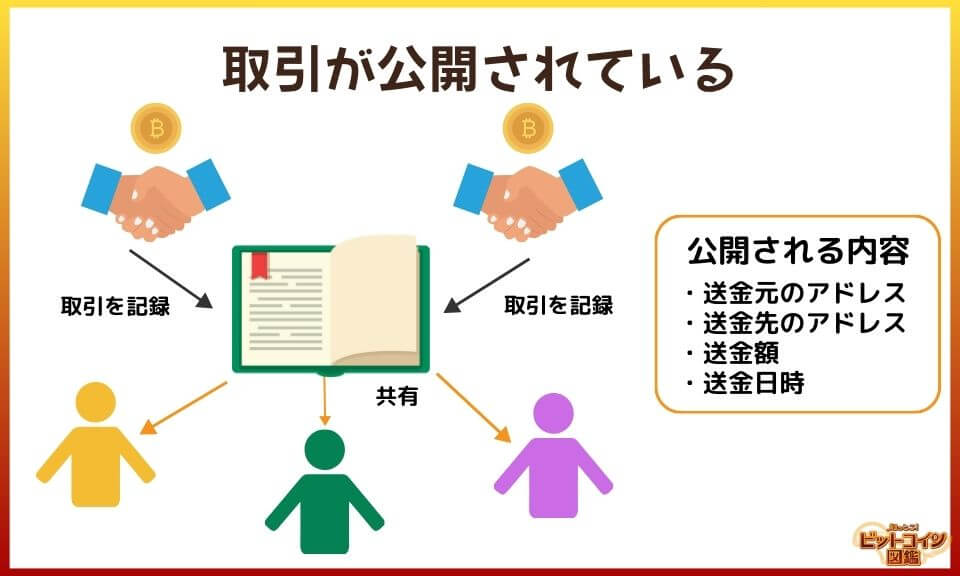
All transactions on the Bitcoin network are public and can be viewed by anyone with an Internet connection.
This transparency allows for tracking of past transactions, a feature that distinguishes Bitcoin from traditional financial systems.
The transaction details that are made public are the source and destination addresses, the amount transferred, and the date and time of the transfer, and individual names are never displayed.

What are the benefits of having the transactions made public?
For example, I can check to see if the bitcoins I donated to the disaster area have reached the destination wallet address, and I can also see how the destination address is moving the bitcoins.
You can also prevent "unauthorized diversion and misuse by centralized administrators" that can occur in the traditional financial system.

How Bitcoin Mining Works


I heard that Bitcoin has a "mining" mechanism…
To put mining in a nutshell, it's the process of checking the transactions that take place on the bitcoin network and writing them correctly into the blockchain.
The people who participate in mining are called "miners" and are responsible for keeping the bitcoin network secure.

The first miner to approve a miner gets a reward.
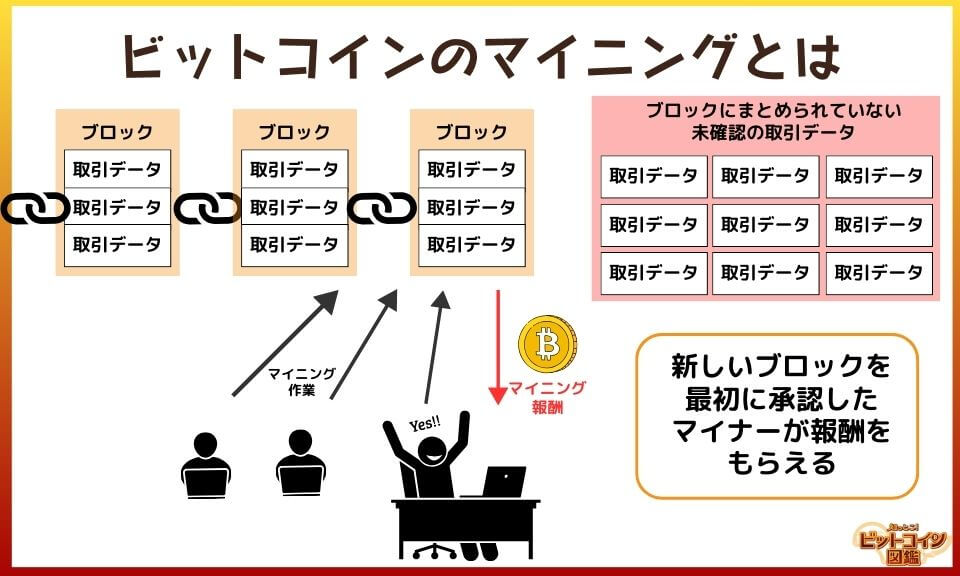
Miners who perform mining use computers with high computing power to perform mining.
Repeating hash calculations while changing the nance in the block, the first miner to find a hash value below the target adds the block to the blockchain.
*Nance: Number used only once
*Hash value: Irregular value obtained by hash calculation based on the created block
The reward for this is bitcoins for newly generated bitcoins and transaction fees.
The reward system creates an incentive for miners to contribute to the bitcoin network and keeps the network secure.
Mining Flow
- Collection of transactions
→Collect unconfirmed transactions made on the network - Verification of transactions
→Verify that the sender has sufficient bitcoin, that the same bitcoin has not been used before, etc. - Formation of blocks
→Collect verified transactions as a block of data - Adding blocks to the blockchain
→Continues to calculate large numbers of transactions until it finds a number that matches the criteria
The first miner to find a value receives newly generated bitcoins and transaction fees.

How many times a day does mining take place?
New blocks are being created every 10 minutes.
That's about 144 blocks per day.

The issuance limit is 21 million coins

Bitcoin has a pre-established issuance cap, and no more than 21 million bitcoins will be created.
The issuance cap prevents inflation (a decrease in the value of a currency) caused by over-issuance, which can be seen with legal tender.
Because there is a cap on issuance, bitcoin is considered to have a scarcity like gold, which helps to preserve its value.

But miners are mining because of the newly generated bitcoins, right?
Is there a possibility that no one will stop mining once the issuance limit is full?
Even after reaching 21 million coins, miners will still get paid by transaction fees.
If the use of bitcoin increases in the future and the total amount of transaction fees increases, that might keep them incentivized enough to do some mining.


Hmmm. By the way, how many bitcoins are issued now?
There are already over 19 million coins issued.


Eh! So most of them have already been issued?
So will you be done issuing new bitcoins soon?
The pace of issuance decreases with each half-life.
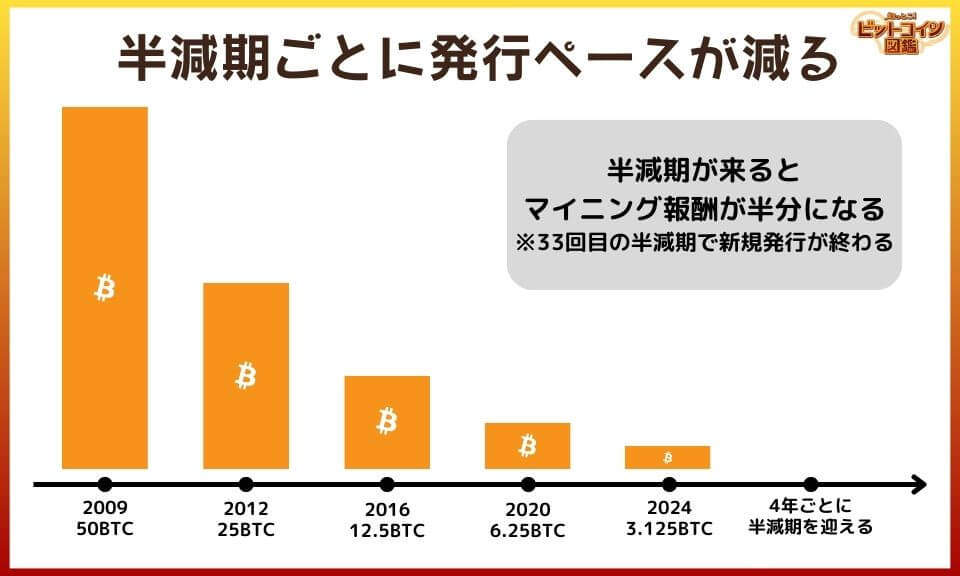
Bitcoin has a "half-life" during which the pace of new issuance decreases.
When the half-life of bitcoin arrives, the pace at which new bitcoins are created is halved.
The half-life occurs approximately every four years and is designed to occur automatically.
Effects of the half-life
- Prevention of inflation
→The pace of new bitcoin issuance is gradually reduced, stabilizing the currency's value over time - Impact on miners
→Miner rewards from mining will be reduced to half, which may cause more miners to withdraw from mining
→Some people believe that the price of bitcoin will be affected by miners selling their bitcoin holdings - Impact on the market
→Some people believe that the supply of bitcoin will decrease, which will "increase scarcity and thus affect the price".

So the initial mining reward is 50 BTC, and the reward is decreasing with each half-life.
I guess that means that after the half-life in 2024, the mining reward will be 3.125 BTC.
By the way, the last bitcoin half-life is expected to be around 2140.
Bitcoin will have a total of 33 half-lives.


2140 years! So over a long period of time, the remaining bitcoins will be generated little by little.
[Intermediate level] A Deep Dive into the Bitcoin Mechanism


I'd like to know a little more in depth about how bitcoin works.
From here, I'll start with a book by Tetsuyuki Oishi, an expert on Bitcoin, titled「ビットコインはどのようにして動いているのか?」I will explain it as clearly as possible with reference to the book.

General Byzantine Problem
In computer science so far, the "Byzantine General Problem" has stood in the way of the development of decentralized networks.
The Byzantine General Problem refers to the situation in which "when one wants to reach a consensus in a system without a central administrator, it is impossible to correctly form a consensus if there is someone who spreads false information.
If there is a central administrator, the administrator can deal with false information, but this is not the case in the absence of a central administrator.
However, Bitcoin provides a solution to the Byzantine General Problem through a realistic and practical mechanism.
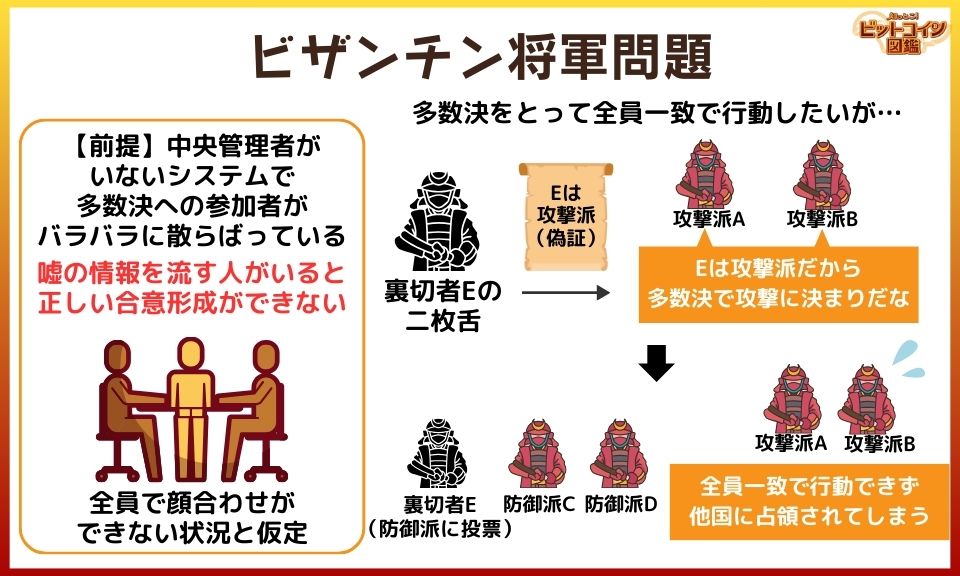
Byzantine General Problem (Example)
- There are 5 generals and they make a majority decision to "attack" or "defend" against a foreign invasion.
- If they don't line up, they will be invaded by a foreign country.
- You cannot all face each other and make a majority decision.
- You can convey your will by messenger, or hear the will of other generals through messengers.
Some of the five are traitors who have been bought off by the enemy and are plotting to disrupt the majority vote
In the above image, the traitor E is
In the case of the above image, E, the traitor, sent the following message.
Message from E to attackers A and B: "E is an attacker.
Message from E to defenders C and D: "E is a defender.
The attackers A and B were fooled into thinking that since E was the attacker, A, B, and E would have a majority, so they decided to attack, and only A and B went to battle.


Hmmm, how can you properly make a majority decision with a traitor in the room, without even meeting him face to face?
It seems to me that there would have to be an absolute central leader, or rather, a governing body.
I know it seems difficult, but there is a solution.
After listening to the intentions of the other generals, we now exchange information about who said what to each other.
For example, Warlord A might tell the other warlords that "A, B, and E are the attackers, and C and D are the defenders.


Sure, that way you can tell that the traitor E is talking crazy!
But how does this story connect to Bitcoin?
Now let's replace the warlord with a computer.
If there is no centralized management system, then a malicious computer can cause problems such as "double payments."

Double Payment Problem
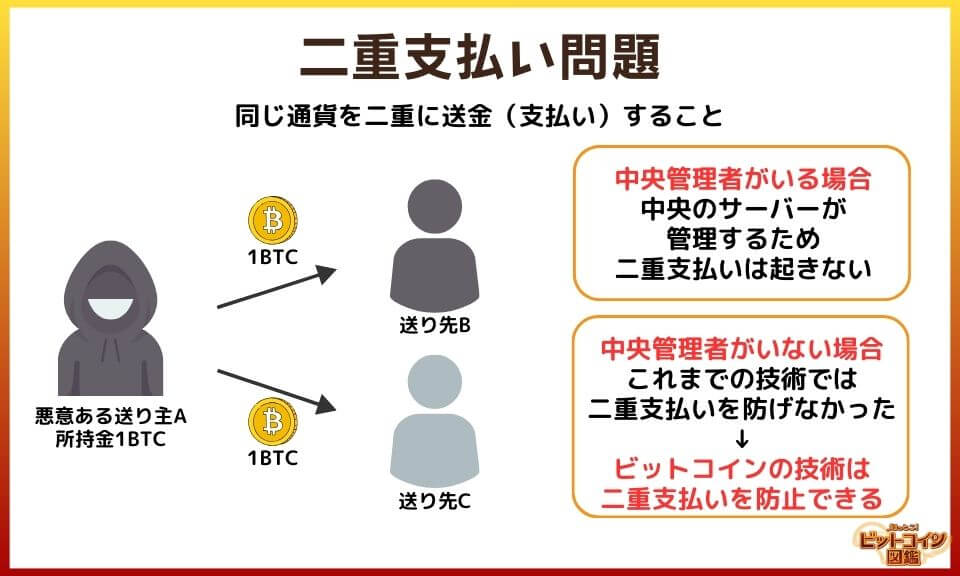
A classic example of lying by a malicious computer is "double payment.
For example, sender A (money in possession: 1BTC) is in the following situation.
I'm A, and I'm going to send 1BTC to Mr. B.
I'm A, and I'm going to send 1BTC to Mr. C.

So A only has 1 BTC, but A falsified the computer information and made the same payment twice!
Unlike the warlord's example earlier, the actual computer can be out of communication, and the number of participating computers is huge, so what can you do?
In digital currency, it used to be difficult to prevent double payments without a central controller.
But with the bitcoin system, there can be only one correct agreement between all the computers in the world.

How to prevent double payments
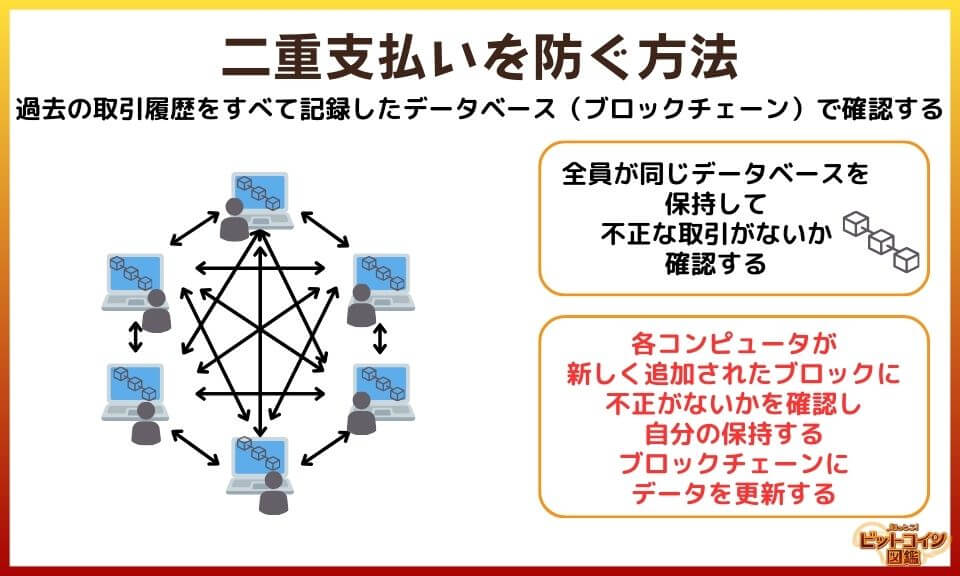
Bitcoin refers to a huge database (blockchain) that keeps track of all past records to make sure there are no double payments.
The blockchain contains all transactions made by all computers and is checked against past transactions to make sure there are no discrepancies.

Oh, so all I have to do is create a database…that's easy.
…Huh? But how can we create such a database if we don't have an administrator?
Each computer would keep a copy of the database at their place and maintain each one.


Can you do that? Who can guarantee that the contents of the databases each has will be the same?
And who has what authority to update the database? And what's more, it might contain lies?
If all the computers could collaborate and "agree" on the Byzantine General issue, the agreement would be the database.
Mining" plays an important role in creating the data for the consensus.

How to Maintain the Bitcoin Blockchain


How does Bitcoin's huge database (blockchain) work?
It's the only database that all computers can agree on, right?
It's a little difficult to explain because of the jargon, but I'll try to explain it as concisely as I can.
Let me start with the "hash function," which is indispensable for a deep understanding of mining.

Hash Functions
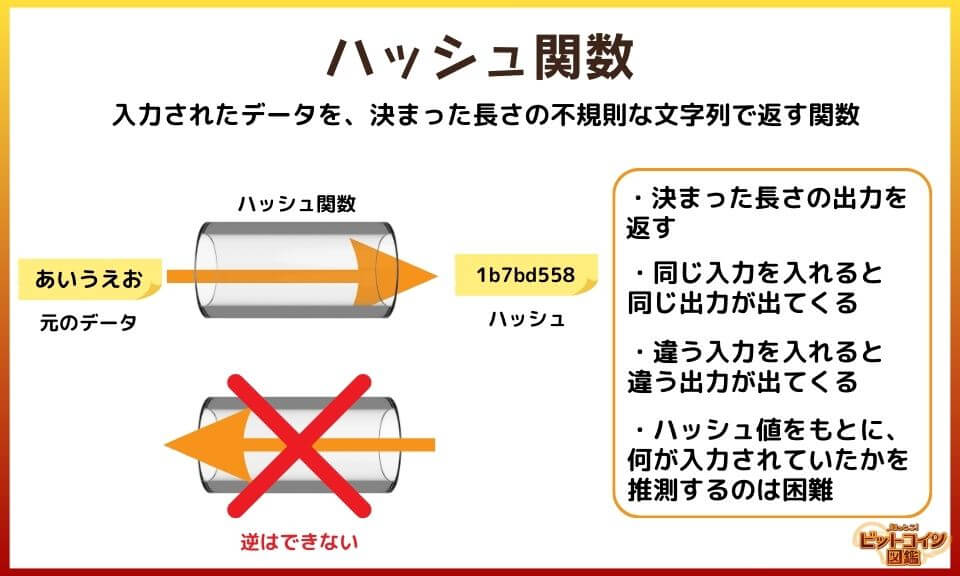
A hash function is a function that returns input data as an irregular string of a fixed length.
Hash Function
- Returns an output (hash value) of a fixed length
- The same output comes out when the same input is put in. No matter who puts in the same input, you get the same output
- If you put in different inputs, you get different outputs. The same hash value cannot be obtained from different inputs.
- Based on the hash value, it is difficult to guess what was input (so difficult that it cannot be expressed at all at the level of trillions of parts per trillion or something like that)

It is astronomically impossible to get to the original input from the hash value of the mystery string! So it's like.
Next, let's look at how Bitcoin uses the properties of the hash function to create a chain of data that cannot be tampered with.

The hash value mechanism prevents tampering.

To ensure that the blockchain can never be tampered with, a hash function is inserted in between to make the blocks intensely associated with each other.
Concept of Blockchain Mechanism
- The transaction data of block 1 is put together and put into a hash function to obtain a hash value
- The hash value of the previous block 1 and the transaction information of block 2 are added together and put into a hash function to obtain a hash value.
- The hash value of the immediately preceding block 2 is added to the transaction information of block 3 and put into the hash function to obtain the hash value.
- Arranging the hash values

When you create a new block, you're mixing in one previous hash value!
For example, even the slightest tampering with the transaction data in block 1 can change the hash value as if it were a different hash value.
This mechanism is surprisingly resistant to tampering.


But if you tamper with one and get caught, why not just tamper with everything after that?
The inventor, Satoshi Nakamoto, came up with an even more clever idea.
He made the calculation of the hash value even more difficult so that it would take a lot of computer power to tamper with it.

Making the calculation of hash values more painstaking (introduction of PoW)

PoW (Proof of Work) is a mechanism that makes the calculation of hash values even more arduous.
A parameter called nonce (nance) is added to the hash value calculation.
There are approximately 4.3 billion possible nance values, and the process must be repeated through trial and error.
When a hash value with leading zeros is obtained, mining is successful.
Every 10 minutes, miners from all over the world repeat the calculation to find the value, and only the first one to find the hash value is considered successful.
The companies that participate in bitcoin mining have a huge array of high-powered computer equipment with huge prices and power costs.
It's very impractical for someone with malicious intent to keep tampering with them.


By making the calculations so hard, you're making sure the bitcoin database can't be tampered with!
Mining
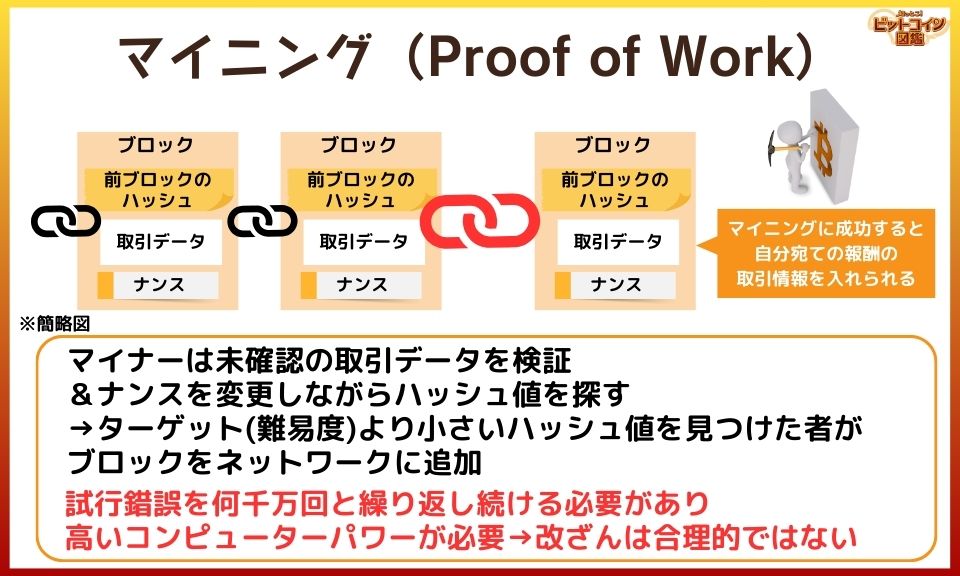
The miner who does the mining just keeps changing the nance and repeating the calculation until a hash value with a large number of zeros is found.
Block generation
- Searching for hash values while verifying unconfirmed transaction data & changing nance
- The first person to find a hash value that matches the criteria can create a new block with the transaction data
- Using the hash value found, block information including Nance and hash value is notified to other computers
The block can include a record of the transaction, sending bitcoins to the bitcoin address of the first miner found
Computers that received the block information
- Checks to see if the hash value is the one found, based on the information from the previous block and the new block
- Checks all transactions in the block for irregularities
- If there are no problems, the computer updates the end of the blockchain (database) it maintains with the new block

So each computer checks for new blocks and updates the blockchain it holds on its own!
In Bitcoin, you form agreements in units of one block every 10 minutes to maintain a decentralized database.

If a malicious block is created
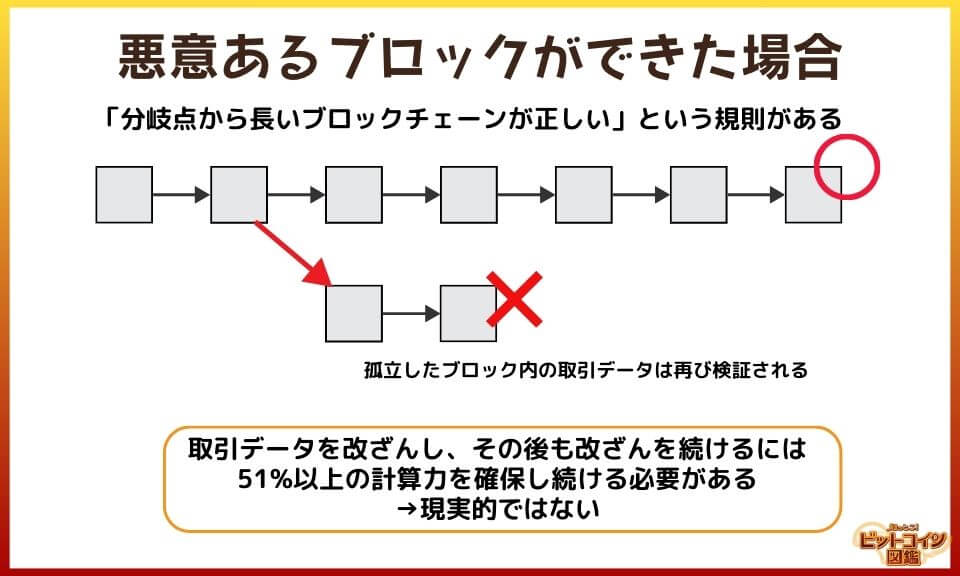

But what if there is a problem with the new block?
If the block contains unauthorized transactions, we will not consider it as an agreement of the network and will not incorporate it.

If a malicious person tries to disrupt the network and create a block that contains strange transactions, there will be two blocks, one malicious and one correct.
Of the two blocks that exist in divergent form, only the correct block will be added to the blockchain, and the network will automatically lengthen.
In order to keep doing the bad stuff, we need to keep at least 51% of the computational power of the entire mining operation.
Right now, the amount of computing power being applied to mining all over the world is so tremendous that it is very impractical to have 51% of the computing power available.


Even if they succeed in hijacking, if they do that, people will stop trusting bitcoin, and bitcoin might lose its value.
I think it would be better to use that power to mine bitcoin than to spend a lot of effort and money to do something bad.
The content introduced in this article is only a rough explanation of a small part of the Bitcoin mechanism, and may be insufficient for advanced Bitcoin users.
[Summary] How Bitcoin Works

summary of key points
- Decentralized network with no central administrator
- Blockchain technology is difficult to tamper with
- Bitcoin network is maintained by mining

Bitcoin doesn't have a "Bitcoin Corporation" or anything like that, it's a "decentralized network" where people and organizations around the world can freely participate in its operation!
It is very difficult to tamper with transaction data, and the transactions themselves are open to the world.
It is a currency with new characteristics that have never existed in legal tender before.


I was kind of nervous about bitcoin because it sounds kind of difficult and I don't really know what it is, but I wanted to know more about it.
I want to know more about Bitcoin!
Recommended Articles:What is Bitcoin?

Writer:Sigeru Minami
Creator of "Bitcoin-zukan.com."
Active as a handmade craftsman of Bitcoin goods.
