

What is Proof of Work?
Proof of Work (PoW) adopted by Bitcoin is an innovative mechanism that can prevent malicious attacks on a network without a central administrator.
However, some media descriptions can lead to misunderstandings about PoW, causing cryptocurrency beginners to feel that "PoW is an outdated and inferior technology."
In this article, we will explain the features of Proof of Work and the differences between PoW and PoS in an easy-to-understand manner.

Summary
- Proof of Work (PoW) involves performing a large amount of computational work, while Proof of Stake (PoS) involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency to obtain the right to create new blocks.
- PoW is criticized for the possibility of a 51% attack, but attacking Bitcoin would require enormous costs and is not guaranteed to succeed, making it unrealistic.
- PoW is criticized for its high electricity consumption, but mining operators are shifting to cheaper power sources to remain profitable, increasing the use of renewable energy.
This article was written in Japanese and converted to English using a translation tool.
Date of writing (Japanese version): February 2024
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
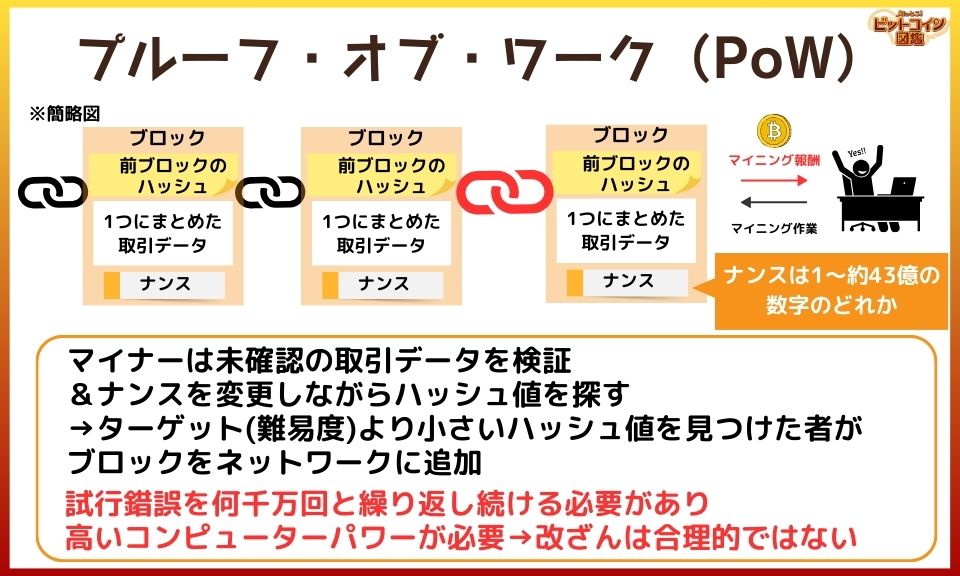
Proof of Work (PoW) is a method of proving the work done to enhance network security.
PoW was introduced in Bitcoin to create a trustless network that operates without an administrator.
The process of performing the computational work in PoW is called "mining," where miners repeatedly perform hash calculations while changing the nonce in the block.
*Nonce: a number used only once.
The first miner to find a hash value below the target can add the block to the blockchain and receive rewards in the form of newly generated Bitcoin and transaction fees in Bitcoin.
*Hash value: an irregular value obtained by performing hash calculations based on the created block.
Main Cryptocurrencies Using PoW
- Bitcoin
- Litecoin
- Bitcoin Cash
- Ethereum Classic
- Monacoin
PoW requires a large amount of computational work to maintain decentralization and prevent malicious attacks.


The reward system motivates miners to contribute to the Bitcoin network!
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
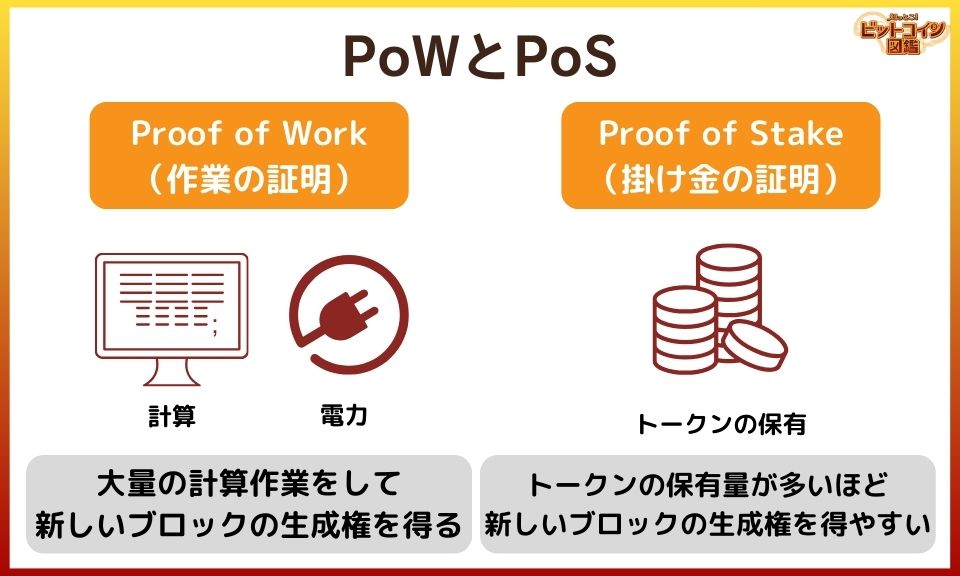
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a mechanism where those who hold a large amount of cryptocurrency are more likely to gain the right to generate new blocks.
By performing "staking," where you lock your currency in the network, you can receive rewards based on the amount and period of the lock.
Compared to PoW, PoS consumes less electricity and is often introduced as a more environmentally friendly new mechanism.
Main Cryptocurrencies Using PoS or Improved PoS
- Ethereum
- Cardano / ADA
- Solana (PoH)
- Polkadot (NPoS)
Holders of PoS tokens can participate in governance voting regarding the network's operational policies.
The more tokens you hold, the greater your influence in governance.


The idea that those who hold more tokens have more influence on the project is somewhat similar to the concept of stocks.
Receiving dividends by holding tokens also feels similar to stocks.
Issues Pointed Out About Proof of Work (PoW)


I heard that there are some problems with Proof of Work…
There are issues that media and cryptocurrency projects point out as "problems with PoW."
However, some of these claims are intended to create a negative impression of PoW to promote PoS tokens. It's important to know the facts about what is being said about Bitcoin's PoW.

Possibility of a 51% Attack
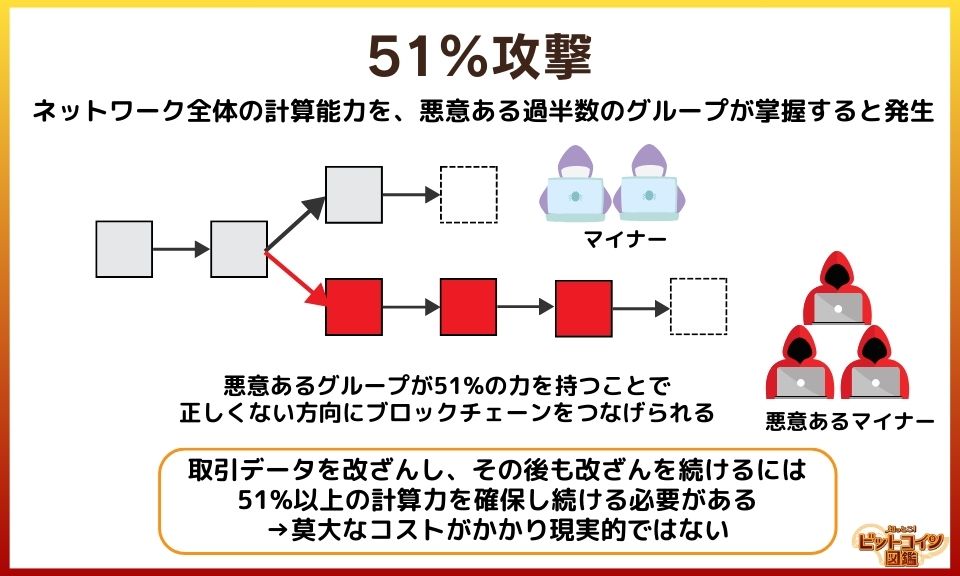
A 51% attack is when malicious miners control 51% of the hash rate, allowing them to execute double-spending.
*Hash rate: The computing power per second for mining.
The hash rate of the Bitcoin network is extremely large, making it technically and economically difficult to control a majority of the network's hash power.
Costs Required for a 51% Attack on Bitcoin
- Renting the hash rate needed for an attack for an hour would cost hundreds of millions of yen, and the network would return to normal once the attack stopped.
→ The blocks created by the attacker would be invalid, so they would have to continue attacking indefinitely. - A massive number of mining devices (such as ASIC miners) are required.
→ It is extremely difficult to assemble a vast number of high-performance machines. - Power and operational costs
→ Maintaining enormous hash power requires a vast amount of electricity, cooling systems, and maintenance costs.
Some experts believe that a 51% attack would require hundreds of billions of dollars.
This is equivalent to the annual budget of a mid-sized country, and carrying out such an attack, with no guarantee of success, is not realistic.

Regarding Mining Pools
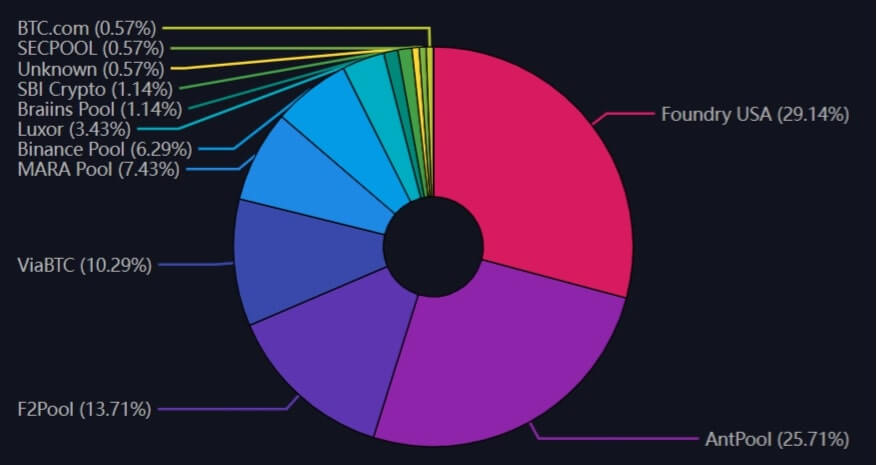
(Surveyed on December 23, 2023)
Additionally, there are claims that "combining the top 2-3 mining pools would allow for a 51% attack, meaning Bitcoin is centralized," but this argument is somewhat exaggerated.
*Mining pool: A mechanism where small-scale miners cooperate in mining and share the revenue.
Miners themselves choose the mining pool they join. If a mining pool were to initiate an attack, miners could choose to leave the attacking pool and join a non-attacking one.
It is practically unrealistic for thousands of miners within a pool to unite and intentionally carry out an attack.

If a 51% attack occurs, the price of Bitcoin held by miners would plummet, and it's hard to believe that all miners would agree to the attack…
Moreover, if a mining pool plans a 51% attack, miners opposing the fraud would likely leak information, making it difficult to unite.
About Power Consumption
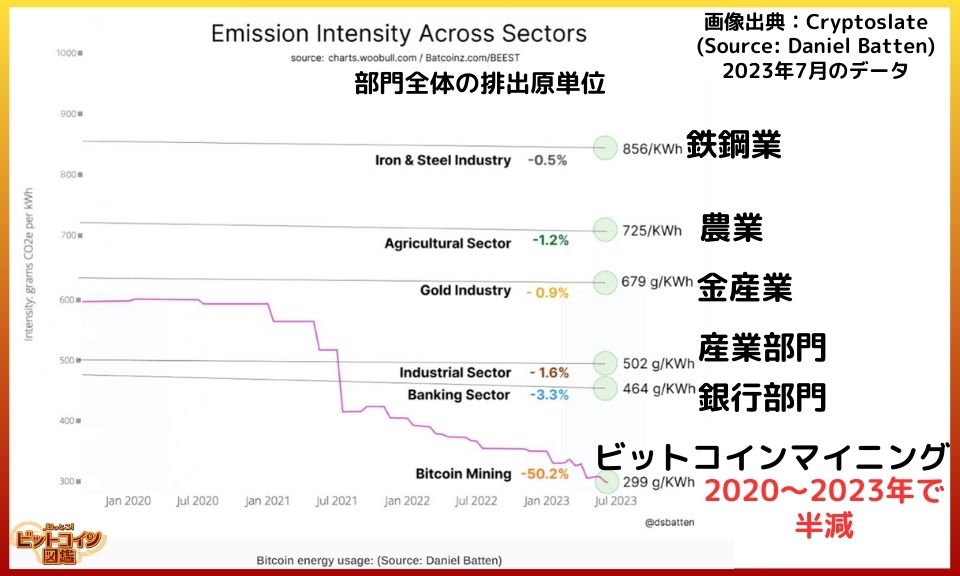
Proof of Work (PoW) requires a vast amount of machine power, and "high electricity consumption" is a frequently raised concern.
However, efforts to reduce power consumption are also underway, and the emission intensity (CO2 emissions per activity) has significantly decreased over the past few years.
Additionally, Bitcoin has a lower emission intensity compared to other financial assets.
*In the US, Bitcoin is classified as a commodity like gold or oil.
Increasing Use of Renewable Energy
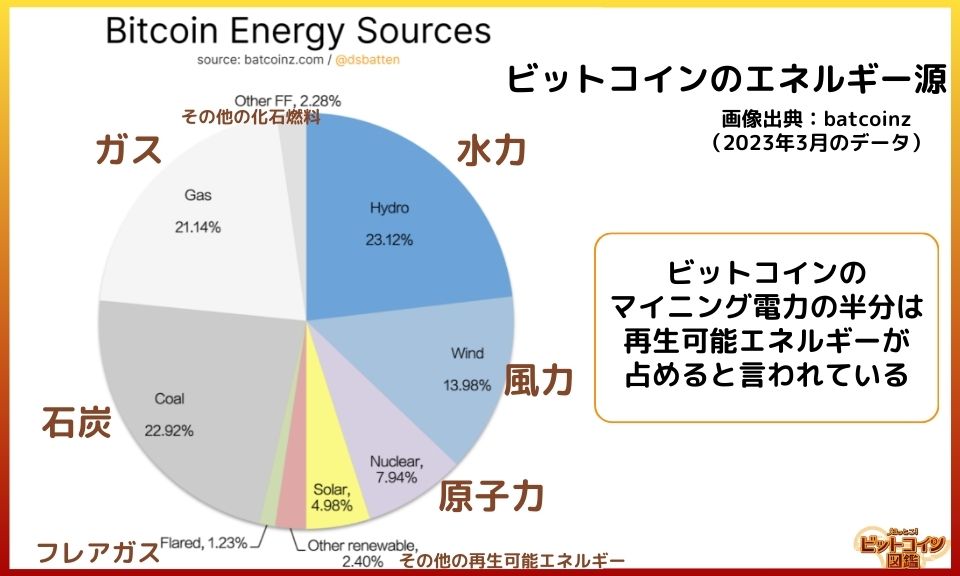
It is said that half of the electricity consumption for Bitcoin mining comes from renewable energy.
Mining operators need to choose the cheapest electricity to make a profit, leading to an increased use of surplus renewable energy that would otherwise go unsold.
Mining is Conducted in Various Countries
- Bhutan: Utilizes abundant hydropower resources from the Himalayas.
- Paraguay: Uses surplus power from the Itaipu Dam.
- USA: Employs flare gas (excess gas from oil fields) for mining in Texas.
- Kenya: Combines mining with small hydropower plants to provide sustainable electricity to villages without stable power (conducted in a way that minimally impacts the local ecosystem).
There are increasing cases where surplus electricity from renewable energy, which is affected by seasons and weather, is used for Bitcoin mining.
Since mining rewards decrease with each halving and there are many competing miners, it seems likely that "seeking cheap electricity" will become more prevalent.


I didn't know that Bitcoin mining could contribute to the development of the renewable energy sector.
If the use of surplus electricity to convert into Bitcoin savings becomes widespread, it could spark innovation in various regions and fields!
Barriers to Participating in Mining
There are concerns that "participating in Bitcoin mining has high barriers," and it is true that purchasing high-performance mining equipment and cooling systems, as well as electricity costs, are necessary.
However, some individuals participate in mining pools or do personal mining, and it is easier to participate in regions with low electricity costs.
On the other hand, becoming a validator* in PoS requires a large number of tokens.
*Validator: Nodes that verify data recorded on the blockchain.
For Ethereum, which is the most well-known PoS, 32 ETH is required for staking to become a network validator.
(32 ETH… approximately 13.68 million yen as of February 16, 2024)

Not only PoW but also some PoS cases have high entry barriers.
I googled Bitcoin mining machines, and they ranged from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of yen, so it might not be entirely impossible for ordinary people if they are in areas with low electricity costs.
By the way, PoS uses a staking pool mechanism for staking, and rewards are distributed based on the amount of tokens held.
In PoW mining pools, rewards are distributed according to the computing power provided to the pool, not the amount of currency held.

About Transfer Speed
On the Bitcoin main network, blocks are generated approximately every 10 minutes, and it is true that transfer speeds can slow down during network congestion.
In PoW, since miners compete in calculation work, there is a probability that blocks will be added at the same timing, requiring multiple block confirmations for transaction safety.
However, technologies like the "Lightning Network," which omits on-chain confirmation for Bitcoin, are also advancing.
Lightning payments, which are fast and low-cost, can be conveniently used for small purchases.
*Lightning Network: A technology that processes transactions outside the Bitcoin blockchain.
Lightning Payments Complete in Seconds
#Bitcoin #Lightning⚡️ payment spotted at Cafe in Gimhae-si in South Korea🇰🇷pic.twitter.com/TUr4ZzhhRN
— Lightning Network+⚡️ (@BTC_LN) March 5, 2023

The payment at the store is completed in an instant!
Using on-chain for large amounts and Lightning Network for small payments might become more common.

Differences Between PoW and PoS

What are the differences between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS)?
Most media only mention things like power consumption differences or the risk of 51% attacks…
PoW and PoS are fundamentally different mechanisms.
While some aspects are complex, Japanese media often don't cover these details, so it's good to know.

Whether Block Producers Bear Risks
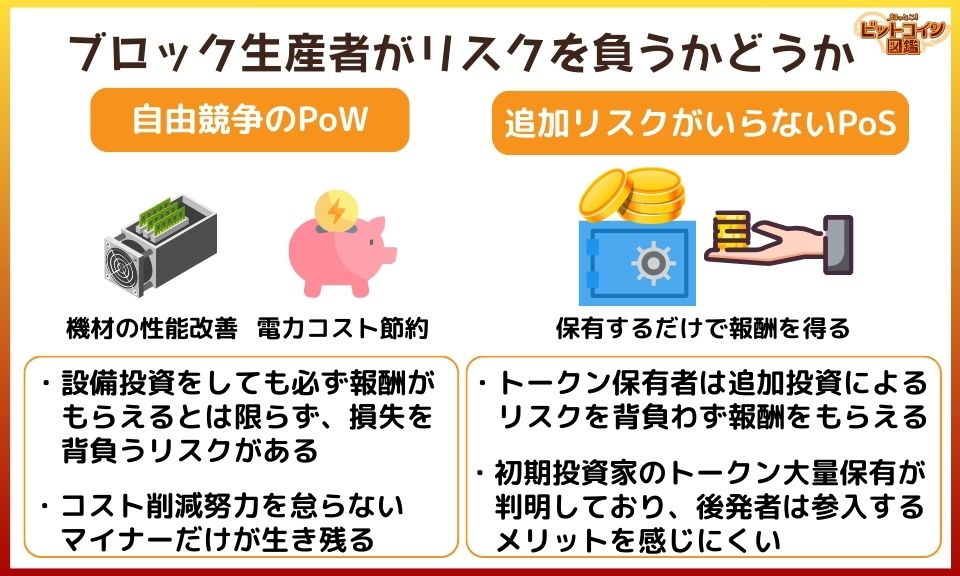
To issue PoW Bitcoin, energy from "outside the coin economy," such as mining equipment and power consumption, is necessary. Additionally, mining is a competitive process, and unless miners succeed in calculations, the costs of equipment and power are wasted.
On the other hand, PoS allows obtaining new coins by holding the coins, without incurring additional costs. Institutional investors with many pre-mined coins face less risk while still earning rewards.
*Pre-mining: Early developers or selected participants receive newly issued tokens before they are publicly available.
- PoW: Value comes from outside the world of the coin. Some believe that real-world resources are consumed and the value of new coins is partially backed by these costs.
- PoS: Value circulates within the coin economy, with potential dilution each time new coins are issued (increased coins through staking may lower the value of each coin).
While there may be opinions that PoS involves the risk of price drops despite having no costs for acquiring new coins, PoS risks are confined within the coin itself and are not linked to the outside world.


PoS, with its lack of external factors, is somewhat uncertain under extreme conditions. It depends on internal actors behaving correctly, so special attention is needed during market crashes or attacks.
PoW Bitcoin has proven resilient against market uncertainties, surviving events like the Mt. Gox incident (850,000 BTC lost) and the Big Block Debate (Bitcoin Cash hard fork).
Keep in mind that PoS is still a new technology and its behavior hasn't been fully validated.

Influence of Large Token Holders
PoW coins do not allow large holders to directly influence the network. For instance, MicroStrategy holds about 1% of Bitcoin's supply but cannot participate in the mining process.
In contrast, PoS gives large token holders significant influence over the network. They can affect protocol changes and updates through governance voting, and the more tokens held, the more they can participate in block generation and earn token rewards.
Voting Whales** (large token holders) have a substantial impact on governance votes.
- Solend Crisis: A governance vote granted Solend Labs emergency powers due to a single user borrowing $107 million. A voting whale's approval made the vote pass.
- Uniswap: In a vote for deploying Uniswap V3 on the BNB Chain, venture capital firm a16z, which holds a large amount of UNI, cast 15 million votes against the proposal. This was reportedly due to the exclusion of a16z's investment "LayerZero" in the bridge.
- Mango: A hacker stole DeFi tokens "MNGO" and manipulated governance votes using the stolen tokens.
PoW Bitcoin does not grant rewards or governance voting rights even to large holders.


Those who hold many PoS tokens stand to gain more block rewards as the network grows and transactions increase.
It might benefit those running validator nodes or companies to attract new users… Be cautious of promotions touting attractive staking rewards.
Ease of Issuing Custom Tokens
When new cryptocurrency projects are launched, the PoS mechanism is often adopted. PoW requires a large amount of computing power and energy to issue new coins, which can be a significant barrier for new projects.
On the other hand, PoS maintains the network through staking by token holders, significantly reducing the cost of launching new projects.
There are projects where custom tokens are issued in a way that benefits the development team or institutional investors.


For small startup companies, issuing tokens might be feasible even if issuing shares is difficult…
PoS projects that are easy to issue might proliferate while using marketing strategies like airdrops (token distribution).
Author's Opinion: Discrepancy in Japanese Media's Approach to PoW and PoS
When you search for articles comparing PoW and PoS on Google, many articles suggest that PoS is newer and superior to PoW. Additionally, some Japanese cryptocurrency exchanges only mention the disadvantages of PoW without listing the disadvantages of PoS in their currency introduction articles.
On the other hand, overseas exchanges like Binance and Kraken provide information on the disadvantages of both PoW and PoS, highlighting a difference in media approaches between Japan and abroad.
Kraken's Description
The main downside of PoS consensus mechanisms is stake centralization issues.
In PoS blockchains, the amount of tokens a person stakes primarily determines their likelihood of being selected to validate blocks of transactions and earn rewards. Because of this, PoS systems could favor those with more tokens over those with fewer staked assets — which some feel leads to centralization of the network.
Because of this flaw, many feel that a small number of large staking pools and whale investors could gain centralized control over block validation. This factor goes against the core principles of cryptocurrency and reduces overall network security.
Another issue for some PoS blockchains is illiquidity. Sometimes, users cannot access their staked assets until a lockup period ends. This problem reduces the market liquidity of the underlying cryptocurrency and prevents investors from being able to access their staked funds during critical market movements.
出典:Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake|Kraken

The amount of information you get from Japanese and overseas media is completely different…
If you only look at Japanese media articles, those who know nothing might just think, "PoS is better."
Since cryptocurrency exchanges handle many PoS cryptocurrencies, it may be difficult for them to write about the disadvantages of PoS…
However, I think it would be more beneficial for users looking for information if they clearly stated the disadvantages, as Kraken and Binance do.

[Summary] What is Proof of Work (PoW)?

Key Points
- Proof of Work (PoW) involves performing extensive computational work, while Proof of Stake (PoS) grants the right to generate new blocks by holding cryptocurrency.
- PoW has been criticized for the possibility of a 51% attack, but attacking Bitcoin would incur enormous costs and is not realistically feasible.
- PoW is often criticized for its large electricity consumption; however, mining operators are shifting to cheaper electricity to maintain profitability, and the use of renewable energy is increasing.

I often see media articles saying "PoW is bad for the environment, so PoS is better!" But I think we should also be well-informed about the current state of PoW and the issues with PoS.
The issuance of Bitcoin with PoW requires mining equipment and electricity consumption, and miners take on the risk of not always receiving rewards.
Additionally, be aware of the potential for innovations in various regions and fields, such as mining systems that provide electricity to small villages in Africa.


Bitcoin seems quite complicated and I don't understand it well, which makes me a bit anxious. But now, I feel like I want to learn more about it.
Let's learn more about Bitcoin!
Recommended Articles:What is Bitcoin?

Writer:Sigeru Minami
Creator of "Bitcoin-zukan.com."
Active as a handmade craftsman of Bitcoin goods.
